KoyaQuest
About Mt. Kōya

About Mt. Kōya

About Mt. Kōya
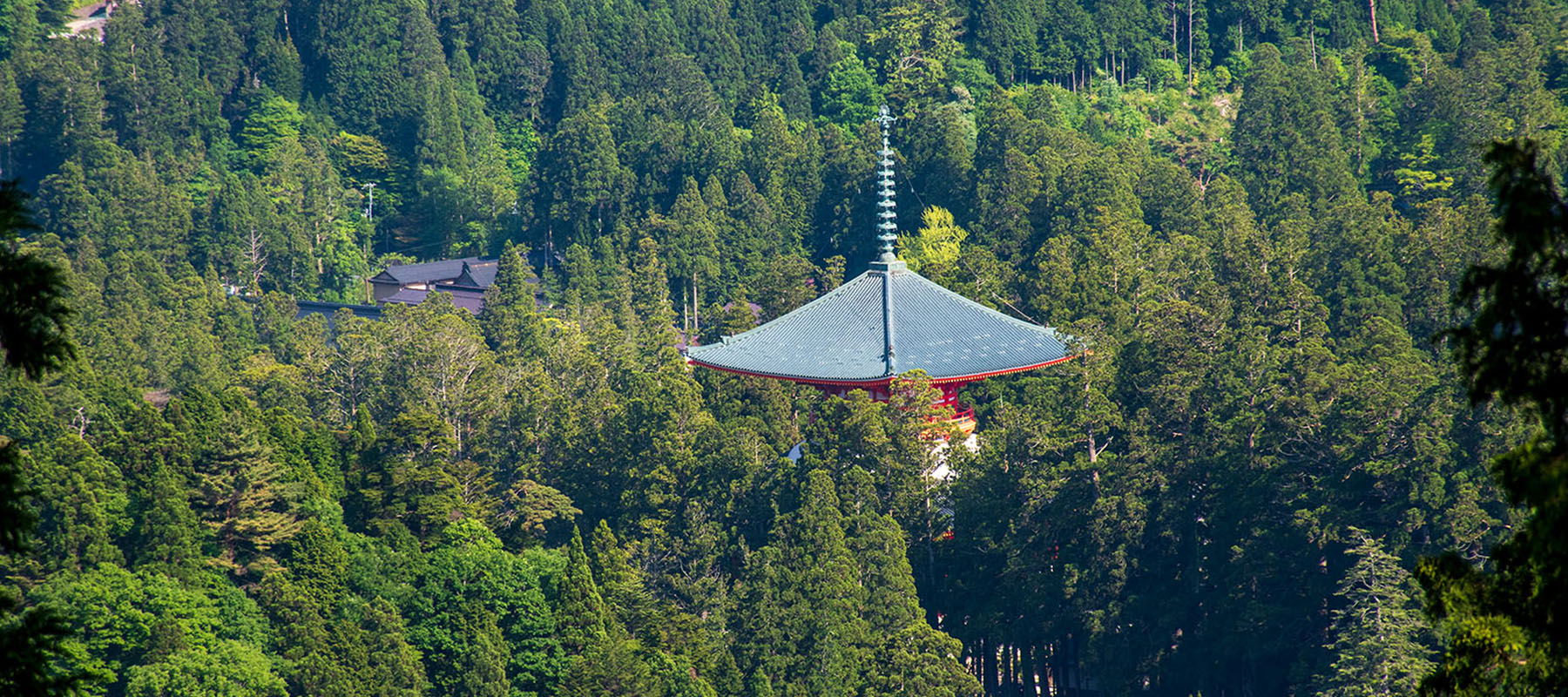
Situated in the mountains of Wakayama Prefecture, two of hours south of Kyoto, Mt. Kōya is home to an active monastic center founded more than 12 centuries ago for the study and practice of Esoteric Buddhism.
As the headquarters of the Kōyasan sect of Shingon Buddhism and the resting place of its founder, it is one of the most sacred places in Japan.
Kūkai, the founder of Mt. Kōya, wanted to establish a sacred space high in the mountains yet affording no view of the world below. The eight peaks that surround the plateau of Mt. Kōya call to mind the eight petals of a lotus blossom upon which the Celestial Buddha sits. These physical features were ideally suited to Kūkai's intention to make his temple a living mandala.
To pass beyond the Great Gate of Mt. Kōya is to enter into a world dominated by the pursuit of spiritual enlightenment.

The small tableland of Mt. Kōya is approximately 4 kilometers in length and less than 2 kilometers broad. In this relatively compact area are more than 117 temples, many of which provide lodging for overnight guests.
Small as it is, Mt. Kōya can be divided into two major areas.
The first of these two areas centers on the Danjō-garan, which is the ceremonial center of the ecclesiastical complex.
This is where one finds many of the halls and pagodas conceived by Kūkai in his original plans. It is where most of the important religious services are conducted.
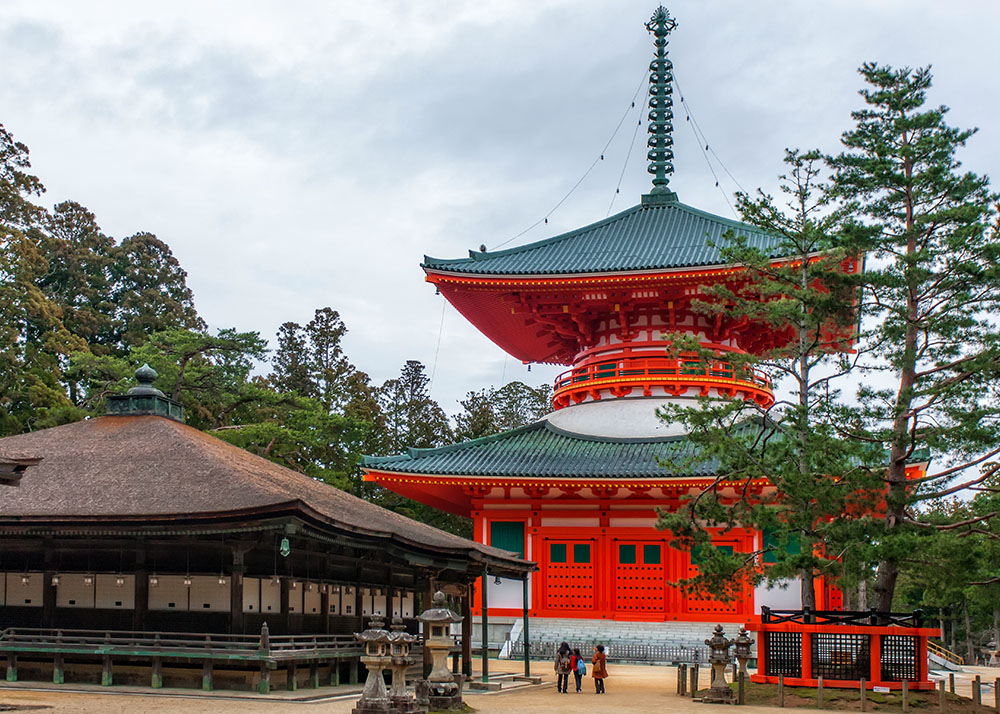

Nearby the Danjō-garan is the temple known as Kongōbuji. This sprawling temple serves as the chief administrative headquarters for more than 3,000 Shingon temples throughout Japan.
The second major area of Mt. Kōya is the vast cemetery that sprang up at the eastern end of Mt. Kōya after the death of Kūkai.
This area is known as Oku-no-in, or "Inner Sanctuary," which refers to the mausoleum where Kūkai is interred. Over the centuries, thousands of Japanese have had their spiritual monuments erected here in order to be near Kūkai to await the arrival of the future Buddha, Maitreya who is believed to appear here at Oku-no-in in 5.6 billion years.
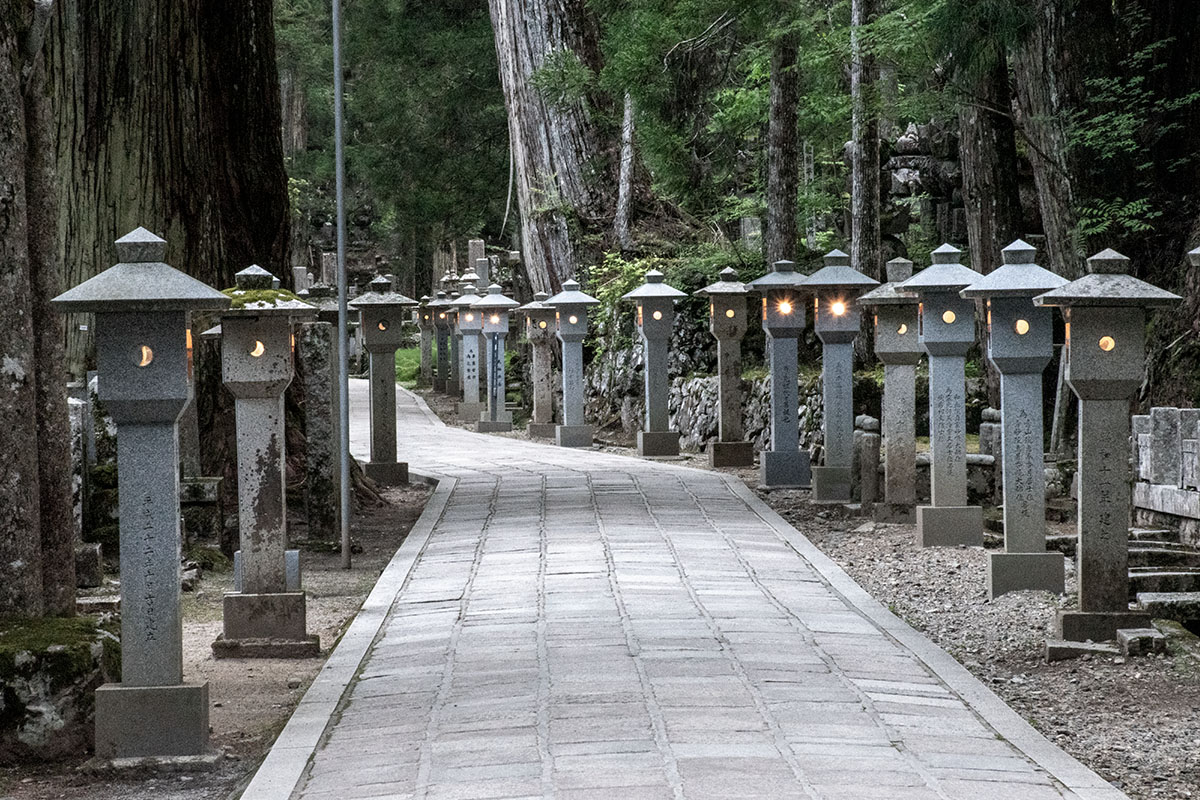

The 1.6 kilometer path that leads to the sanctuary is lined with thousands of moss-covered stone monuments and hundreds of massive Japanese cedars, creating an unforgettable blend of natural beauty and religious austerity.
In 2004, several temples belonging to Mt. Kōya were included as part of UNESCO's "Sacred Sites and Pilgrimage Routes in the Kii Mountain Range" World Heritage Site. In the intervening years, this quiet ecclesiastical settlement has become one of Japan's more popular tourist destinations.
The tranquility and antiquity of Mt. Kōya were celebrated as early at the 13th century as the following passage from the Tale of the Heike attests:
"Mt. Kōya lies two hundred leagues beyond the capital, separated from towns and villages, where the wind in the treetops replaces the sound of human voices and the sun sets in tranquility. Amid the eight valleys and eight peaks, the heart and mind are refreshed. The colors of the blossoms burst forth beneath the forest mist. The ringing of tiny bells rises to the lofty clouds. Ferns spread out upon the rooftiles, and moss covers the walls, calling to mind the passage of many years."
-- Heike monogatari 『平家物語』
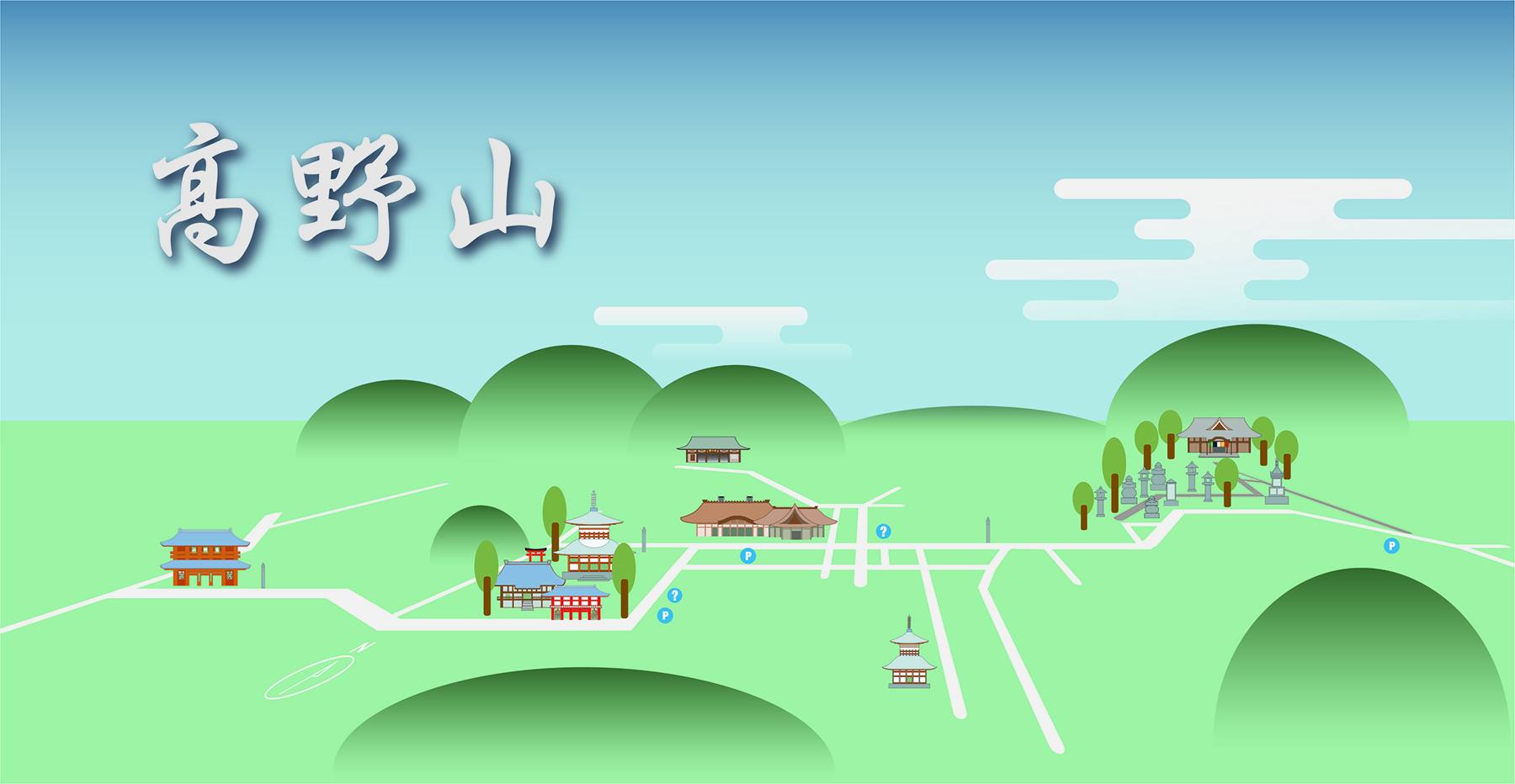
Click to see enlarged, interactive map.
© 2024, k. collins